What is Business Process Management (BPM)?-今日硅谷
BPM focuses on improving corporate performance by managing business processes. Processes used to manage a company’s business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable and unstructured and variable. Though not required, they are often used with BPM.
It can be differentiated from program management in that program management is concerned with managing a group of inter-dependent projects. From another viewpoint, process management includ es program management. In project management, process management is the use of a repeatable process to improve the Outcome of the project.
As an approach, BPM sees processes as important assets of an organization that must be understood, managed, and developed to announce and deliver value-added products and services to clients or customers. This approach closely resembles other total quality management or continual improvement process methodologies ISO 9000 promotes the process approach to managing an organization.
…promotes the adoption of a process approach when developing, implementing and improving the effectiveness of a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements.
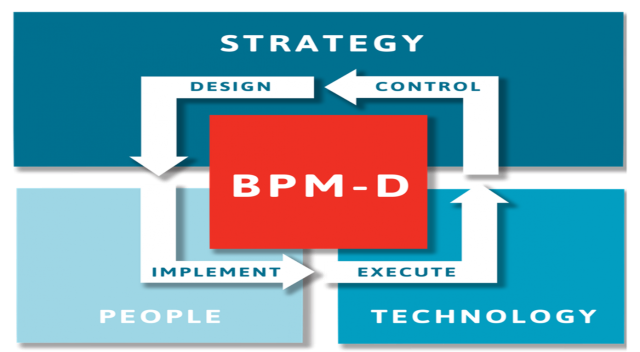
BPM proponents also claimed that this approach can be supported, or enabled, through technology. As such, many BPM articles and scholars frequently discuss BPM from one of two viewpoints: people and/or technology.
Definitions
BPMInstitute defined Business process management as:
…the definition, improvement and management of a firm’s end-to-end enterprise business processes in order to achieve three outcomes to a performance-based, customer-driven firm: 1) clarity on strategic direction, 2) alignment of the Firm’s Resources, and 3) increased discipline in daily operations.
The Workflow Management Coalition, BPM.com and several other sources use the following definition:
Business process management (BPM) is a discipline involving any combination of modeling, automation, execution, control, measurement and optimization of business activity flows, in support of enterprise goals, spanning systems, employees, customers and partners within and beyond the enterprise boundaries.
The Association of Business Process Management Professionals defines BPM as:
BPM relates to the subject of the business process management (BPM) is a disciplined approach to identify, design, execute, document, measure, monitor, and control both automated and non-automated business processes to achieve consistent, targeted results with an organization’s strategic goals. , collaborative and increasingly technology-aided definition, improvement, innovation, and management of end-to-end business processes that drive business results, create value, and enable an organization to meet its business objectives with more agility. BPM enables an enterprise to align Its business processes to its business strategy, leading to effective overall company performance through improvements of specific work activities two within a specific department, across the enterprise, or between organizations.
Gartner defines business process management as:
“the discipline of managing processes (rather than tasks) as the means for improving business performance outcomes and operational agility. Processes span organizational boundaries, linking together people, information flows, systems and other assets to create and deliver value to customers and constituents.”
It is common to confuse BPM with a BPM suite (BPMS). BPM is a professional discipline done by people, heterogeneous a BPMS is a technological suite of tools designed to help the BPM professionals synchronizing their goals. BPM should also not be confused with an Employment and solution developed to support a particular process. Suites and solutions represent ways of automating business processes, but automation is only one aspect of BPM.
Technology
BPM is now considered a critical component of operational intelligence (OI) solutions to deliver real-time, actionable information. This real-time information can be acted upon a variety of ways – alerts can be sent or executive decisions can be made using Real -time dashboards. OI solutions use real-time information to take automated action based on pre-defined rules so that security measures and or exception management processes can be initiated. Because “the size and complexity of daily tasks often requires the use of technology To Model efficiently” when resources in as market information museum (IT) and Business.
There are four critical components of a BPM Suite:
Process engine – a robust platform for modeling and including process rules -enabled applications, business
policies — enable managers to identify business issues, trends, and opportunities with reports and dashboards and reacted associated
Content Management – provides a system for storing and planning electronic Documents, Images, and other files
Collaboration tools – remove intra- and interdepartmental communication barriers through forum forums, dynamic workspaces, and message boards
BPM also addresses many of the critical IT issues underpinning these business drivers, including:
- Managing end-to-end, customer-facing processes
- Consolidating data and increasing visibility into and access to associated data and information
- Increasing the flexibility and functionality of current infrastructure and data
- Integrating with existing systems and leveraging service oriented architecture (SOA)
- Establishing a common language for business-IT alignment
Validation of BPMS is another technical issue that vendors and users must be aware of, if regulatory compliance is mandatory.[33] The validation task could be performed either by an authenticated third party or by the users themselves. Either way, validation documentation must be Generated. The validation document usually can either be published officially or retained by users.
Cloud computing BPM
Cloud computing business process management is the use of (BPM) tools that are delivered as software services (SaaS) over a network. Cloud BPM business logic is deployed on an application server and the business data resides in cloud storage.
Market
According to Gartner, 20% of all the “shadow business processes” are supported by BPM cloud platforms[citation needed]. Gartner refers to all the hidden organizational processes that are supported by IT departments as part of legacy business processes such as Excel spreadsheets , routing of emails using rules, phone calls routing, etc. These can, of procedure also be replaced by other technologies such as workflow and smart form software.
Benefits
of The Benefits of the using BPM Cloud Services includ- E Removing The need and cost of Maintaining Specialized Technical skill sets and in-House Reducing decompositions from AN Enterprise apos main Focus. It Offers Controlled Budgeting and the IT INCURRED The Mobility Related Cross .
The Internet of things the the
emerging Internet of things poses a significant challenge to control and manage the flow of information through large numbers of devices. To cope with this, a new direction known as BPM Everywhere shows promise as way of blending traditional process techniques, With Additional Capabilities to automate the handling of all the independent devices.
